Which customer data is the best of all? Zero-party data.
Why?
Because people voluntarily share this data with the business.
No other data type is more accurate and perfectly reflects the intention and motivation of the customers as zero-party data.
As browsers are phasing out third-party cookies, the demand for zero-party data has skyrocketed, making it a must-have for marketers.
In this blog, I’ll tell you about,
Let’s get in.
Table of Contents
What is zero party customer data?
Zero-party data is information that customers voluntarily and proactively share with a business.
Since this customer data is collected with consent, privacy concerns and compliance issues with privacy laws are none.
This makes zero-party data a superior data source to third-party cookie data, which is collected without direct user consent and often fails to comply with privacy regulations.
Some examples of zero-party data include Email addresses, Survey and feedback responses, Demographic or company information filled during signup or registration, and email message preference stated during the newsletter signup.
A real-time example of collecting and using zero-party data:
ASICS, an e-commerce business selling running shoes and activewear, lets first-time users take a simple survey to find shoes that perfectly fit their needs and preferences.
On one side, ASICS is collecting zero-party customer data, which helps them understand who their customers are, and on the other, a first-time audience can easily find their perfect shoes without scrolling and navigating to multiple pages.
This is the perfect example of zero-party data collection and its effective use to improve customer experience.
Why is it called zero-party data?
The term “zero party”says there are zero steps between the data source (the customer) and the data user (the business).
Customers directly share this data with the business without any intermediaries.
Example: A customer voluntarily completes a survey about their experience using the product on a brand’s website.
Comparing Zero-party data with Other data Types
| Feature | Zero-Party Data | First-Party Data | Second-Party Data | Third-Party Data |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Customers proactively share data with the company | Company collects data directly from customers | Another company shares the data with you | Aggregators collect data from various sources and sell to businessess |
| Source | Customer surveys, preference centers, polls | Company’s own sources (website, CRM, social media) | Trusted partners’ (Company) data (websites, apps, surveys) | Multiple sources from the internet (surveys, interviews, feedback) |
| Collection Method | Customers voluntarily provide information | Direct collection through interactions, surveys | Shared by trusted partners, purchased from sources | Purchased from data marketplaces |
| Accuracy | High | High | High | Variable |
| Cost | Low (voluntarily provided) | Low (collected directly) | Moderate (shared or purchased) | High (purchased) |
| Privacy | High (explicit consent given) | High (consent obtained directly) | High (consent ensured by partner) | Variable (depends on data provider) |
| Data Examples | Preference data, purchase intentions, survey responses | Website interactions, purchase history, CRM data | Same as first-party data | Demographics, interests, Behavior |
| Use Cases | Improving customer experience | Ad retargeting | Audience expansion | Broad audience targeting |
| Ownership | Owned by the company | Owned by the company | Owned by the partner | Owned by data aggregators |
| Risk | Low (voluntarily provided by customers) | Low (controlled by the company) | Moderate (depends on partner’s data practices) | High (variable data quality and privacy concerns) |
Recommended read: 9 data types every marketer should know already
Why Has Zero-Party Data Become So Significant?
1. Privacy Regulations and Compliance
With stricter privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA, businesses must ensure data privacy compliance.
Zero-party data, shared voluntarily by customers, aligns with these regulations, reducing legal risks.
Zero-party data involves explicit customer consent. Because customers share the data by themselves, it meets global privacy standards and builds trust between businesses and consumers.
2. Consumer Trust and Transparency
Transparent data collection builds trust with consumers. Customers who understand and consent to data sharing are more likely to engage openly with brands.
Like the quiz ASICS conducts to help first-time users find their perfect fit shoe
3. Accuracy and Relevance
Customers share the data with the business, making it more accurate and relevant than indirectly collected data, like second and third-party data - Where the data comes from other sources. You don’t even know how precise and quality it is.
Zero-party data is often more current, ensuring businesses use the latest customer information.
4. Enhanced Personalization
Businesses can create highly personalized customer experiences with zero-party data, including customized product recommendations and targeted marketing campaigns.
Personalization driven by zero-party data leads to higher customer engagement and satisfaction - Think about it, Your website traffic engages with one of your polls, where the insights say people are struggling to do better email marketing,
Now, Using the insight, You could create a lead magnet around it and promote it using the popups or any interactive content to website traffic,
What do you think will happen?
The personalized offer can generate high engagement among traffic and get you more leads.
Zero-party data is a real deal.
5. Adaptation to the Cookieless Future
As third-party cookies are phasing out, businesses need alternative data sources.
Zero-party’s direct, most relevant, and accurate customer data can fill the gap and be a reliable data source for the long term.
6. Customer Insights (Image)
In the ASICS ‘Finding the Perfect Shoe quiz,’ after collecting my needs and preferences, the quiz redirected me to the product page, where shoes are personalized to my needs and requirements.
This simple quiz can easily convert people with buying intentions.
It can also inform the business of what type of customers are visiting their store and their preferences and needs.
Which can then be used to create relevant content, write landing page copies, and promote products that sync with the customer.
Strategies for Zero-party data collection
Surveys

Surveys are structured questionnaires given to customers to gather information.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? You can collect opinions, feedback, needs, problems, preferences and other identity information like name, and email address.
Why it’s the best method? Surveys are a direct and efficient way to gather specific customer information. They allow you to ask precise questions and get detailed responses.
Quizzes

Quizzes are interactive content pieces that ask users questions in a fun and engaging format.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? You can gather information on preferences, needs, interests, and other identity information like name, and email address.
Why it’s the best method? Quizzes engage users while collecting valuable data, making it less intrusive. They can also be tailored to match your brand’s voice and style.
Onboarding Forms
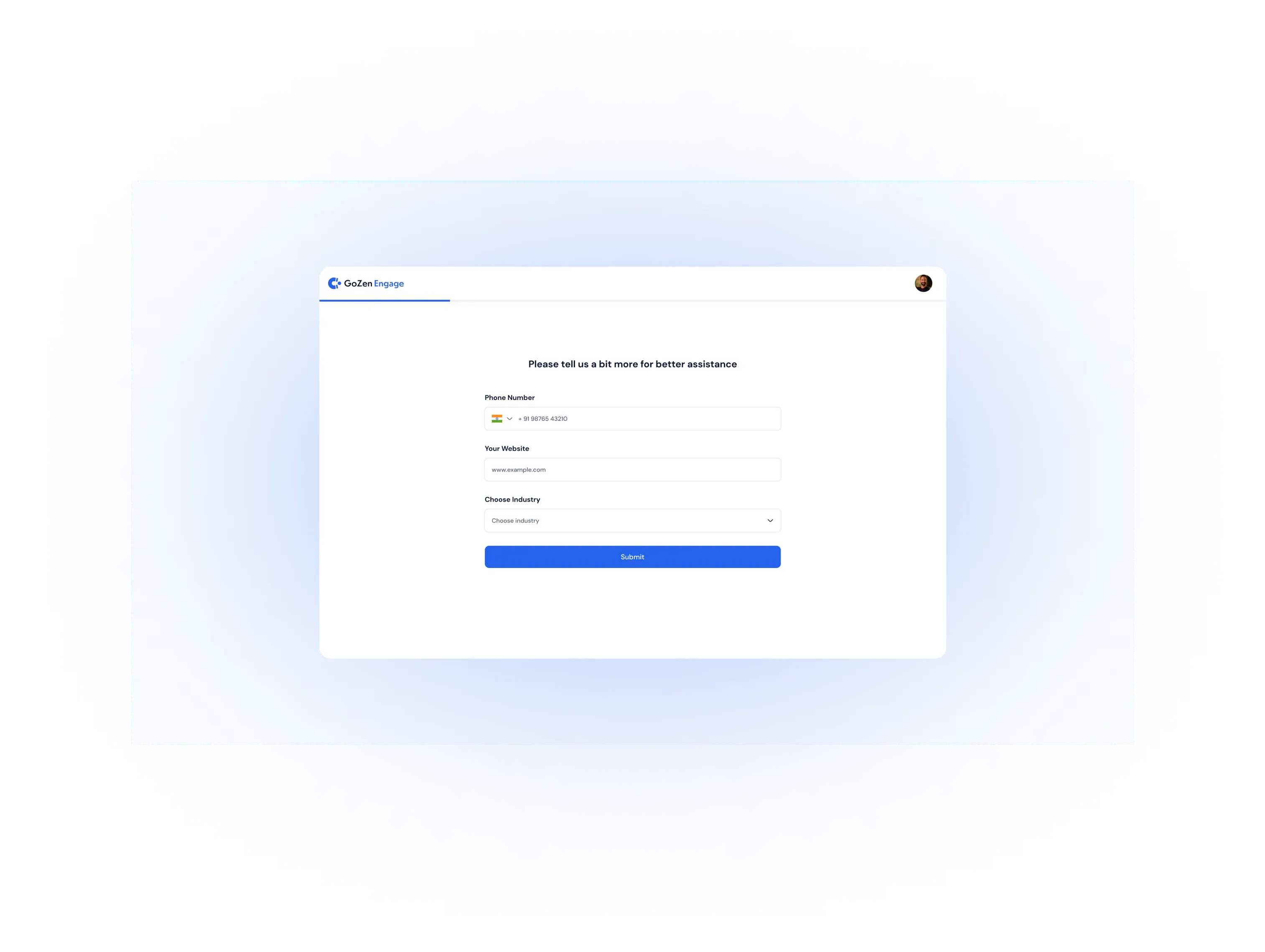
Users or customers fill out these forms after signing up or buying the product.
What data can be collected with this method? You can collect demographic information, roles, company details, and more.
Why it’s the best method? Onboarding forms capture essential information at the beginning of the customer relationship. They help you understand who your customers are from the start.
Interactive Content and Popups

This includes engagement tools like polls, spin-the-wheel, and games.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Gather preferences, likes, and dislikes.
Why it’s the best method? Interactive content keeps users entertained while gathering valuable insights. It can also create a fun and memorable experience for users. Keeping your brand atop of your consumer’s mind.
Loyalty Programs

Programs that reward customers for repeat business
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Collect preferences, demographic information, and purchase behavior.
Why it’s the best method? It creates repeat engagement and provides ongoing data collection opportunities. Customers are more willing to share data in exchange for rewards and benefits.
Events and Contests
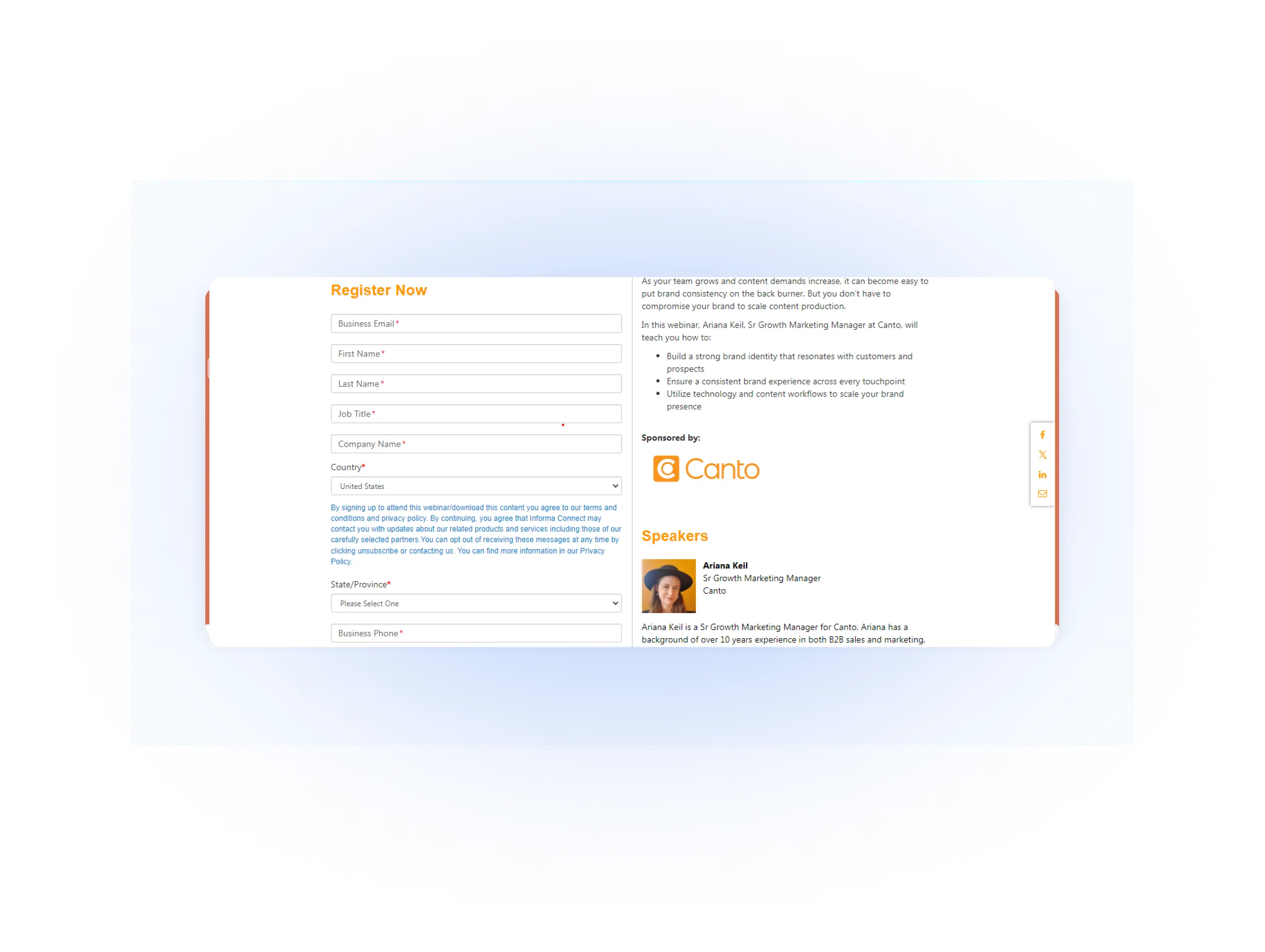
These involve registration forms where participants fill in details to join the event or contest.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Collect demographic information, roles, company details, interests, and motivation to join the event.
Why it’s the best method? Participants are highly engaged and more willing to share information because they are excited about the event or contest.
Customer Support Interaction
This involves customers making direct interactions with customer support representatives.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Customer issues, needs, and preferences.
Why it’s the best method? Provides real-time insights into customer problems and motivations. It also helps build stronger customer relationships.
Social Media Interactive Content

This includes polls, question stickers, and live video sessions on social media platforms.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Gather interests, preferences, and opinions.
Why it’s the best method? High engagement levels on social media make data collection more efficient. It’s also a great way to interact with your audience in real time.
Welcome Surveys
Short surveys included in welcome emails.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Collect preferences for email communication and content.
Why it’s the best method? It captures initial customer preferences right after sign-up, helping you tailor your communication.
Webinar Q&A Sessions
Interactive question and answer sessions during webinars.
What kind of data can be collected with this method? Gather specific problems, interests, and feedback.
Why it’s the best method? Webinars engage an already interested audience, leading to higher-quality data. They also allow for in-depth discussion and interaction.
Tools for collecting the zero-party data
GoZen Forms AI
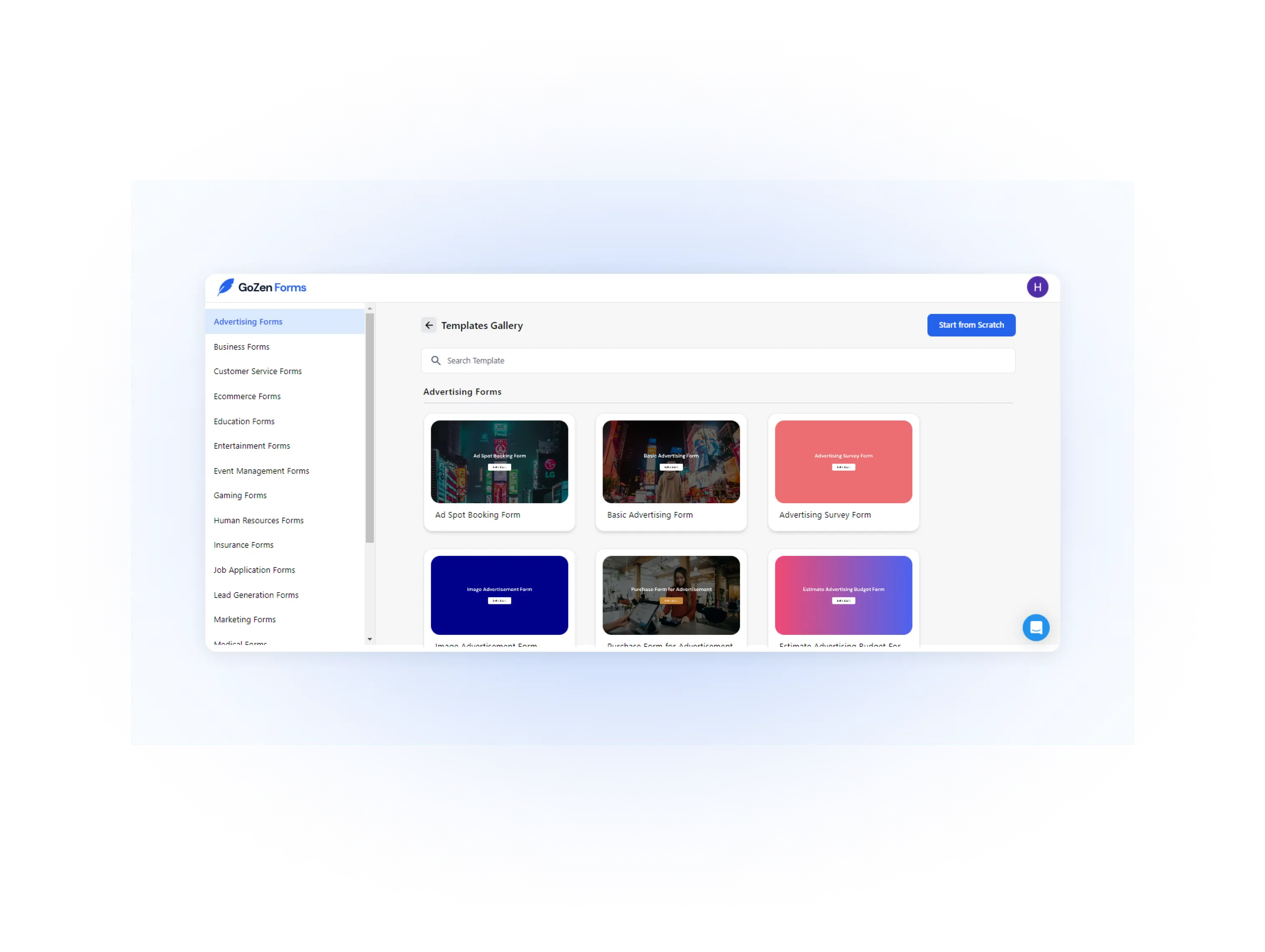
GoZen Forms AI is a no-code form builder that collects data, payments, and e-signatures. It offers customizable forms with conditional logic and an AI-powered form builder.
Features include multi-form view themes, skip logic, and integrations with platforms like Google Sheets and Mailchimp.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: By creating interactive, personalized forms, businesses can directly collect user preferences, feedback, and other valuable data from their target audience.
Pricing:
Optinly
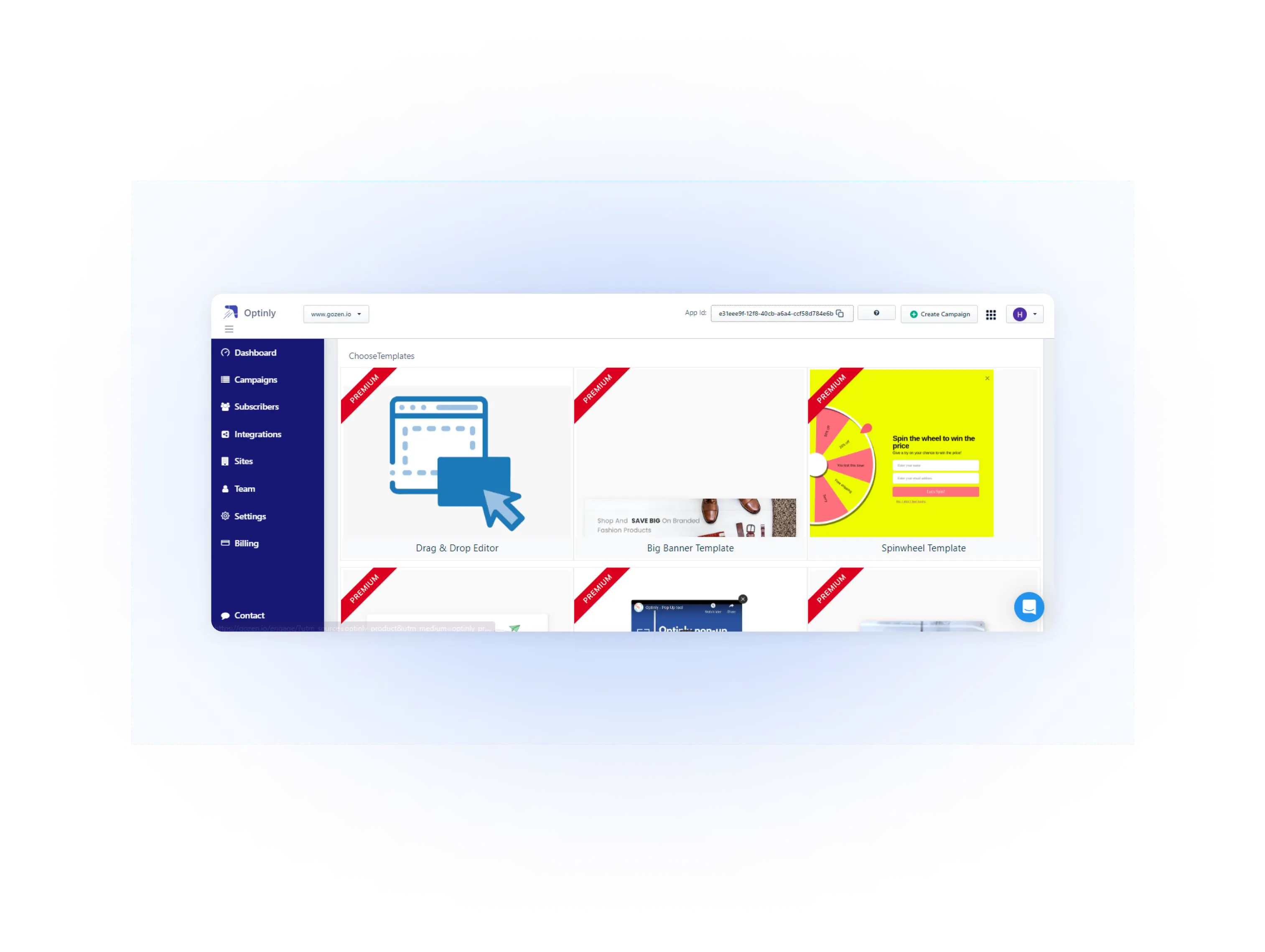
Optinly is a website popup builder designed to engage visitors and monetize traffic.
It allows users to create popups, such as exit intent, slide-ins, and countdown timers, to capture names and email addresses and promote offers.
The tool features a drag-and-drop builder and customizable templates.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: Optinly’s popups can directly ask visitors for feedback and contact information, providing valuable zero-party data through engaging and well-timed interactions.
Pricing:
GoZen Engage AI
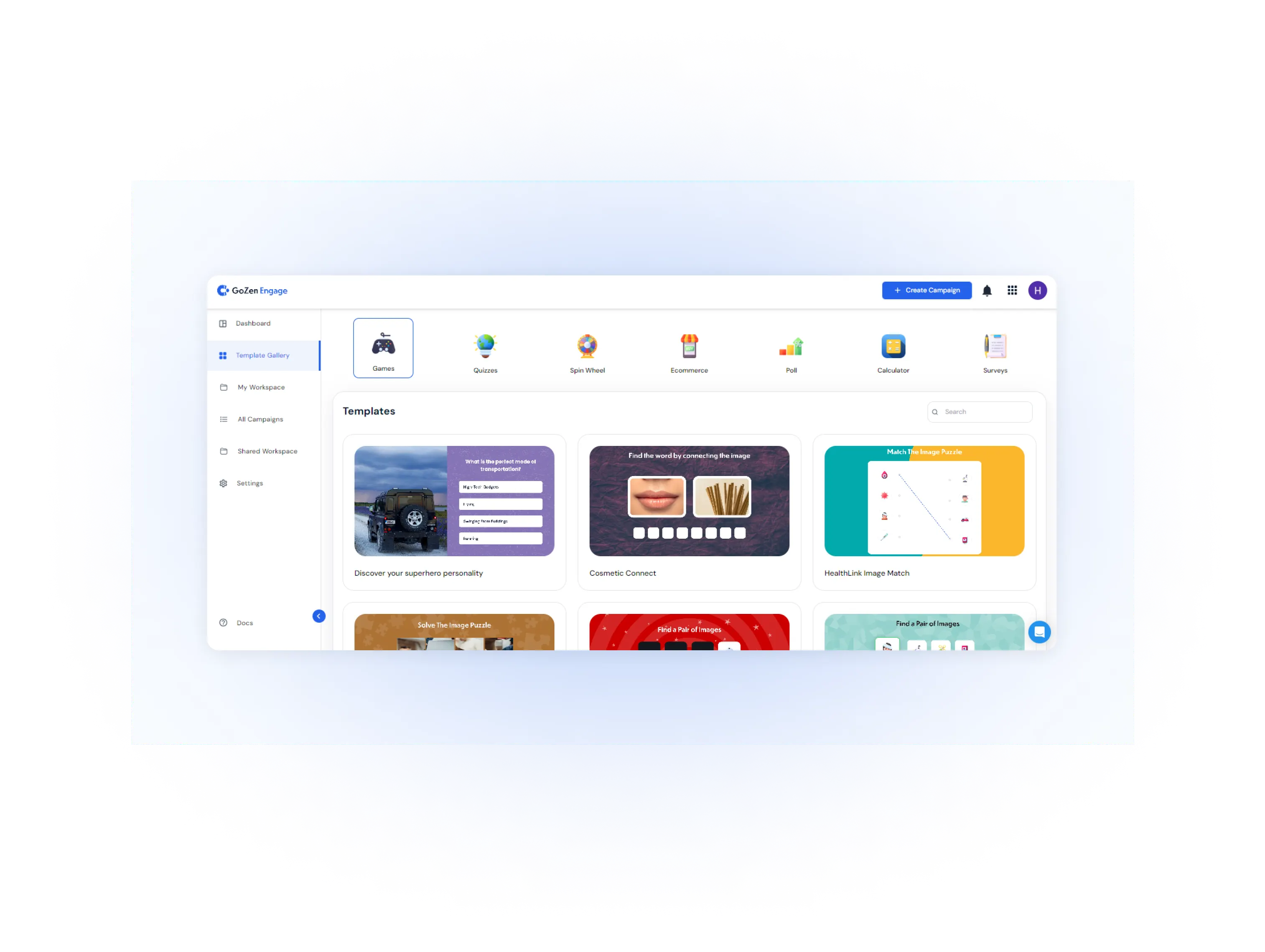
GoZen Engage is an AI-powered tool for creating interactive content and gamification to generate leads and boost sales. It offers quizzes, games, surveys, and polls.
The platform uses AIto develop engaging questions and supports features like gamification, calculators, product recommenders, and custom branding.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: By creating engaging and gamified content, GoZen Engage helps you encourages users to share their preferences and feedback directly through interactive elements.
Pricing:
JotForm

JotForm is an online form builder that helps users create custom forms, surveys, and questionnaires. It offers a drag-and-drop builder with various templates and widgets and integrates with tools like Google Sheets, Slack, and PayPal.
JotForm enables businesses to collect accurate and voluntary customer data.
How it helps to collect zero-party data: Using customizable forms, Jotform enables businesses to directly ask customers for their preferences and feedback, ensuring the data collected is accurate and voluntarily provided by the users.
Pricing:
GoZen Notify
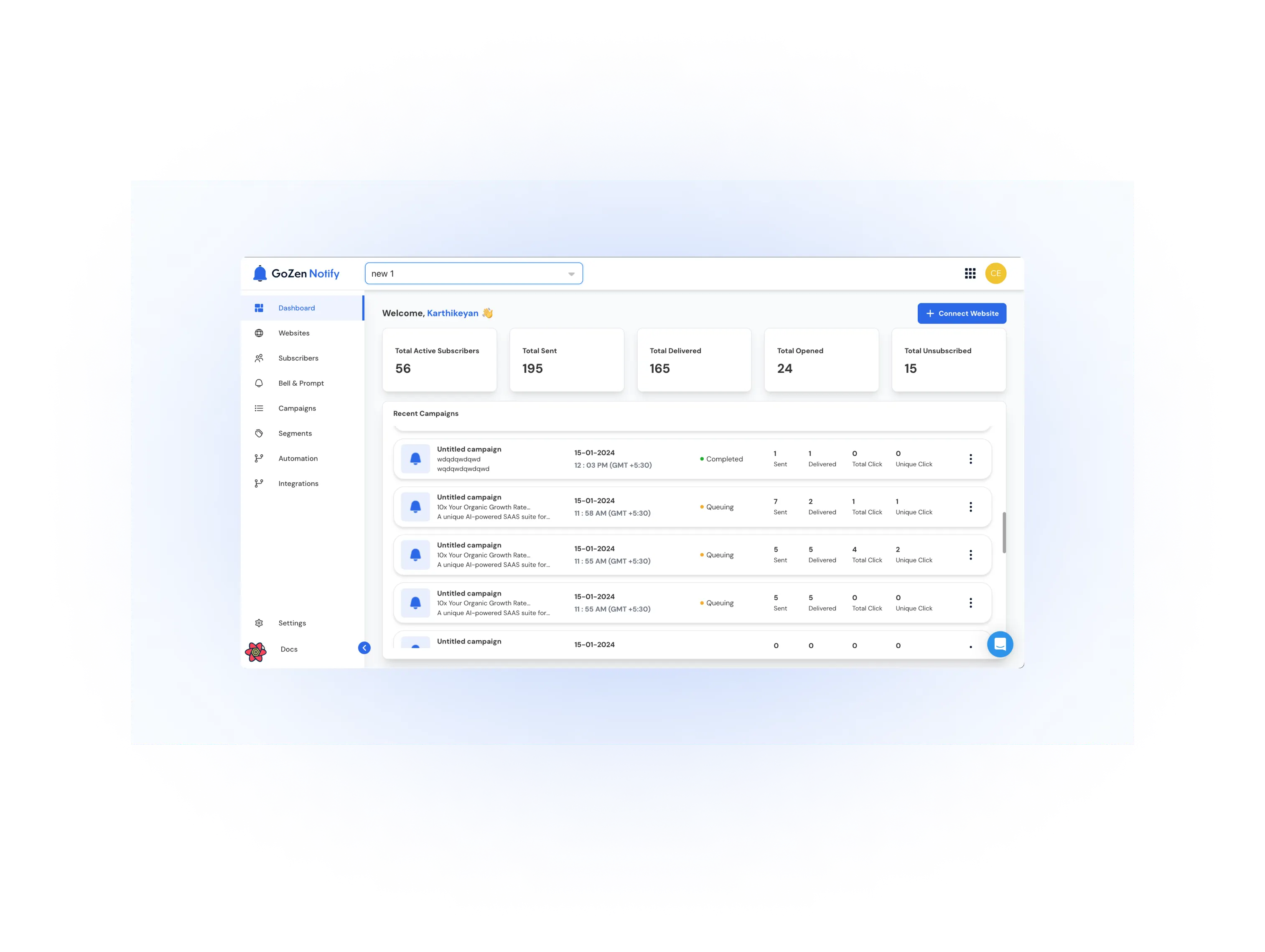
GoZen Notify is an AI-powered push notification software that boosts customer engagement and retention.
It allows businesses to send personalized push notifications for product announcements, blog posts, event alerts, and location-based discounts.
The platform supports automation, targeted notification delivery, and real-time analytics.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: GoZen Notify collects zero-party data by engaging customers with timely website notification messages.
These messages prompt target customers to share their preferences for receiving website notifications, which is valuable zero-party data.
Pricing:
Typeform
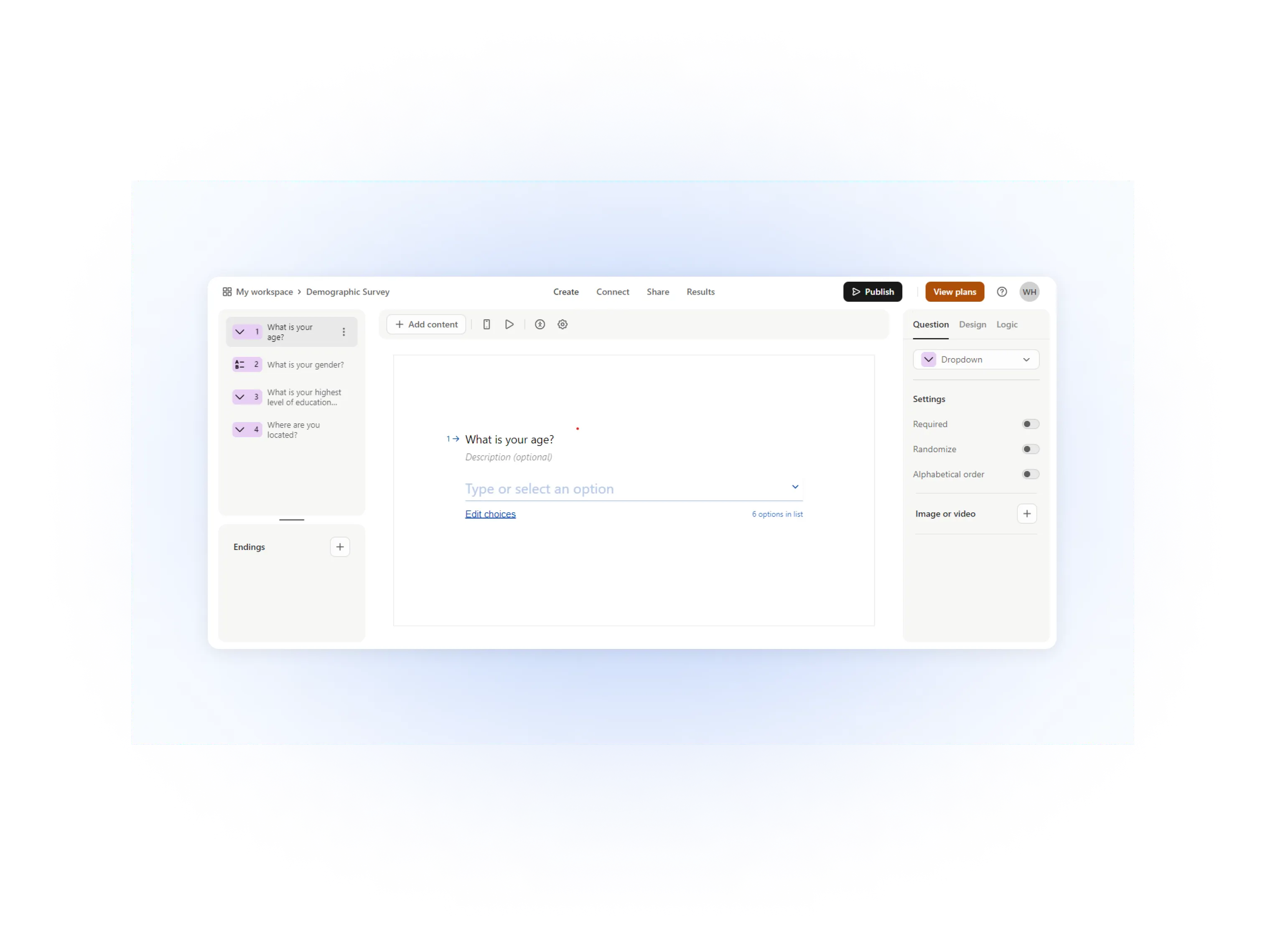
Typeform is a form-building tool that creates interactive and visually appealing forms, surveys, and quizzes.
It asks one question at a time to make the experience more engaging.
Typeform offers numerous templates and integrations to streamline data collection and analysis.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: Typeform’s engaging forms, surveys, quizzes, and polls allow you to gather customer responses, feedback, testimonials, opinions, and ideas, the purest forms of zero-party data.
Pricing:
Google Forms
Google Forms is a free online form and survey builder. It allows users to create simple forms, surveys, and quizzes, integrating seamlessly with other Google services.
Google Forms helps businesses gather user feedback and preferences through customizable forms.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: Google Forms enables businesses to directly gather user feedback, preferences, and other information through straightforward and customizable forms.
Pricing:
Zoom
Zoom is a cloud-based video communications platform for video and audio conferencing, webinars, live chats, and screen sharing.
It enables high-definition meetings, interactive webinars, instant messaging, and content sharing.
How it helps you collect zero-party data: Zoom helps collect zero-party data through interactive methods like polls, Q&A sessions, and custom registration forms during webinars and meetings.
Most importantly, you can use this tool to conduct, collect, store, and use customer interviews, case studies, webinar events, and meetings —your golden zero-party data you can’t get anywhere else.
Pricing:
ConvertKit
ConvertKit is designed for creators to capture their audience and perform email marketing. It provides features for email automation, landing pages, forms, and integrations with other platforms.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: ConvertKit’s popups, landing pages, and online forms help you collect zero-party data like names and email addresses.
Pricing:
Testimonial

Testimonial is a platform for collecting and displaying customer testimonials.
How this helps you collect zero-party data: It allows businesses to gather text and video testimonials —zero-party data —from customers and embed them on websites.
Pricing:
Here’s how GoZen collects zero-party data from customers:
Before launching new products, we give selected customers full access to the product and ask for their feedback.
Since the product is new, we receive a lot of feedback.
Based on its importance, We use the collected feedback to make small and big changes before launching.
After launching, we keep collecting feedback through reviews and customer support from those who have bought and used the product.
Viswa, a full-stack developer at GoZen, says, “I added a new feature in GoZen Engage AI—audio (music) in interactive content—based on a customer’s request through chat support.”
The best way to stay relevant and valuable to your customers is to regularly get feedback and fine-tune your product, marketing, and sales.
What are the challenges in zero-party data collection?
Limited Volume of Data
Zero-party data is collected only from customers who engage with tools like surveys, quizzes, and forms.
This can result in a smaller data pool than first-party data, which collects data from all website visitors.
For example, if 1,000 people visit your website, you can gather behavioral insights from all of them.
However, with zero-party data, if you send a survey to 1,000 people, you might only get complete data from 200-400 respondents.
Investment in Technology
Collecting zero-party data effectively often requires investment in technology platforms such as quiz-building tools, customer data platforms (CDPs), and CRM systems.
These tools are essential for efficiently collecting, storing, analyzing and using the collected zero-party data.
User Engagement and Participation
Getting customers to actively participate and provide their data can be challenging.
High engagement rates are crucial but not always guaranteed.
Encouraging participation often requires creative, engaging content and monetary or related benefits.
Data Quality and Accuracy
While zero-party data is generally accurate, ensuring high-quality and representative data can be complex.
Factors like survey biases can negatively impact the data quality, making it less reliable.
Customer Trust and Privacy Concerns
Building and maintaining customer trust is essential.
Customers need to feel secure when sharing their personal information and understand how it will be used.
Complying with privacy laws and communicating them to your target customers is crucial.
Adapting to Privacy Regulations
Companies must navigate and comply with global data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
These regulations require explicit user consent before data collection, adding complexity to the process.
Creating Engaging Content
Developing interactive content that effectively collects data while providing value and maintaining customer interest can be resource-intensive.
Content like games and quizzes can keep users’ attention and ensure successful data collection.
Data Integration and Utilization
Integrating zero-party data with existing first-party data and other sources to view customer insights as a whole is often complex.
This integration usually requires advanced tools like CDPs, which can handle multiple data types and create meaningful customer profiles for marketing personalization.
Timely and Contextual Data Collection
Identifying the right moments to ask for data, such as during account registration, post-purchase, or through interactive popups, is crucial for maximizing response rates and data relevance.
For instance, asking for an email ID through a discount popup while someone is deeply engaged in reading a blog may not be effective. Timing matters.
How to use the collected zero-party data?
Effectively using the zero-party data depends upon the type of data you collect.
Here are the 14 types of zero-party data you can collect from your target customers.
1. Email preference while signing up for the newsletter
2. Customer support interaction insights
3. Surveys
4. Critical Feedback Related to Product and Service
5. Quiz responses
6. Leads Collected through Popups
7. Responses from Polls
8. Brand, product, and service reviews
9. Website notification preference
10. Interviews and case study
11. Data Through Registration Forms
12. Loyalty program - Purchase transaction data
12. Social media interactions like comments and mentions
13. Questions Asked During Virtual or Online Events
Here’s how to use them in your Business, marketing, sales, and customer support.
Email preference while signing up for a newsletter
Marketing: Your target audience’s email preferences on questions like ‘Would you like to receive educational content or promotional messages from us?’ can help you personalize educational and promotional email messages to match subscriber preferences, increasing open, click-through, and even conversion rates.
Customer support interaction insights
Business: Identify common pain points and areas for improvement in your products or services.
Marketing: Create content, such as FAQs and technical support guides, that addresses frequently asked questions and common issues related to your products or services.
Sales: Equip sales teams with information on common customer concerns to address during the sales process.
For example, one insight gained from conversing with customers on the support side is that ‘People really care about the integration with their existing marketing tools.‘
A salesperson can use this insight and emphasize all the product’s integration options to the customer, thus increasing the probability of converting the prospect into a buying customer.
Surveys
Business: Gain insights into customer satisfaction with products and services and areas needing improvement to further tweak existing product and service offerings.
Marketing: Use the survey data to create content and write copy that speaks directly to target customers’ problems, pains, needs, and preferences. This will increase the chance of attracting traffic and convincing them to take action.
Sales: Understand what drives purchasing decisions to tailor sales pitches.
Customer Support: Identify service gaps and improve support processes.
Critical Feedback Related to Product and Service
Business: Directly integrate feedback into product development cycles.
Marketing: Understand which features or aspects target customers really care about through the critical feedback and highlight those features or aspects in your landing page copy.
Quiz Responses
Marketing: Create highly targeted marketing content based on quiz results. ASICS, for instance, can understand the most sought-after shoes based on quiz responses and create content around them, discussing them on social media to generate engagement.
Customer Support: If the customer support team understands the most sought-after product, they can prioritize preparing for common customer support issues relevant to the product.
Leads Collected through Popups
Marketing: Use the collected leads to send nurturing and promotional emails to move people down the sales funnel.
Responses from Polls
Marketing: Use poll insights to generate content ideas, tweak the landing page copy, and decide on the positioning statement.
The possibilities are limitless; what matters is the theme of the polls you ask and the number of responses you get.
Customer Support: For instance, if you prepare a poll about common customer concerns and the result indicates people are frustrated about slow customer response, you can use this insight to improve your customer support’s quickness in handling queries.
Brand, Product, and Service Reviews
Business: Use reviews to identify strengths and areas for improvement in your product and service.
Marketing: Showcase positive reviews as social proof in campaigns.
Sales: Show positive reviews to build trust with potential customers during sales meetings.
Customer Support: Follow up on negative reviews to resolve issues and improve customer satisfaction.
Website Notification Preferences
Marketing: Send notifications that are highly relevant to user preferences.
If people prefer notifications about blogs, they might also be interested in lead magnets that solve a problem, like an ebook guide.
Use this opportunity to send content that addresses their problems.
Interviews and Case Studies
Marketing: Develop compelling case studies to showcase success stories.
Use the insights from these customer interactions across all your marketing efforts, from idea generation to FAQ question preparation.
Sales: Use case studies to prove your product’s effectiveness during pitches.
Data Through Registration Forms
Marketing: Segment target customers based on the demographic and other insights they’ve provided (like company size, role, etc.) during registration and send relevant email messages personalized to their demographics and other insights.
Loyalty Program
Business: Analyze buying patterns to guide inventory and product development.
Marketing: Create loyalty rewards and targeted offers based on purchase history. Also, send upsell and cross-sell marketing messages based on customers’ past purchases.
Customer Support: Be prepared and ready to handle all customer problems relevant to the most purchased products.
Social Media Interactions (Comments, Mentions, and DM’s)
Business: Monitor brand sentiment and address public feedback about your brand and product.
Marketing: Use the comments to discuss with target customers, analyze their concerns and problems, and directly integrate the insights into your content marketing efforts to create content people love.
Customer Support: Respond promptly to customer inquiries and issues raised on social media.
Questions Asked During Virtual or Online Events
Marketing: Use questions to create content like blogs, videos, and infographics that address common concerns raised during the event.
Sales: Follow up with attendees who asked questions about the product to provide further information and assess their buying readiness.
Customer Support: The customer support team can prepare themselves to answer questions people ask during the event related to the product and easily use the answers whenever the typical questions are asked in chat.
How to protect the data you collect?
Secure Data Storage
Implementation: Use secure data storage systems that comply with industry standards. Choose cloud storage providers with robust security measures, such as data encryption and physical security controls.
Best Practices: Back up data regularly to prevent loss. Ensure storage tools have automatic updates and patches to maintain security.
Implementing cloud computing systems for Secure Data Storage not only ensures robust management but also integrates scalable solutions. Those looking to enhance their understanding can explore comprehensive cloud computing courses that provide insights into better storage and processing methodologies. Harness tools aligned with cloud best practices to secure sensitive information, employ advanced encryption standards, and ensure compliance.
Data Transmission and Processing
Implementation: Use secure methods for data transmission, such as HTTPS for web communications and VPNs like ExpressVPN, for system data transfers.
Best Practices: Employ Transport Layer Security (TLS) to protect data in transit.
Use secure APIs and regularly audit data processing systems for security compliance.
Encryption
Implementation: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit.
Use Advanced Encryption Standards (AES) with strong key management.
Best Practices: Regularly update encryption keys and store them securely.
Use end-to-end encryption for communications containing sensitive information.
Access Controls
Implementation: Use role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive data.
Best Practices: Conduct regular access reviews to keep permissions up-to-date.
Implement least privilege access principles - Granting users only the access necessary for their role .
Regular Security Audits
Implementation: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and assure compliance with security policies.
Best Practices: Conduct security assessment with both internal and third-party auditors.
Take actionable improvements based on audit findings and follow up with re-evaluations.
Identity Access Management (IAM)
Implementation: Use IAM solutions to control data access.
IAM systems manage user identities, enforce access policies, and provide authentication and authorization.
Best Practices: Implement single sign-on (SSO) and MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication).
Regularly review and update IAM policies to adapt to changing security needs.
Protection Against DDoS Attacks
Implementation: Use DDoS protection tools to detect and mitigate attacks on web applications, Data centers, servers, etc.
Employ traffic analysis, rate limiting, and traffic distribution through CDNs (Content Delivery Networks)
Best Practices: Regularly update and test DDoS protection measures. Monitor network traffic for unusual patterns.
Firewalls
Implementation: Use firewalls to block unauthorized access. Configure firewalls to monitor and control network traffic based on security rules.
Best Practices: Regularly update firewall rules. Use both hardware and software firewalls for layered security.
Regular Data Consent Updates and Preferences Tracking
Implementation: Keep data consent preferences up-to-date and provide easy options for customers to modify their preferences.
Best Practices: Maintain a clear privacy policy and use preference centers for updates.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Implementation: Ensure data collection, usage, and storage comply with laws like GDPR and CCPA or the relevant privacy laws in your country.
Best Practices: Conduct regular compliance audits and stay informed about changes in data privacy laws. Consult legal counsel to review data practices.
Educating Employees on Data Privacy
Implementation: Provide ongoing training on data privacy and security. Ensure employees understand protocols for handling sensitive data.
Best Practices: Use training programs, workshops, and regular updates to inform employees about security threats and best practices.
Balancing Personalization with Privacy
Implementation: Use zero-party data for personalization while respecting user privacy.
Avoid collecting excessive information and be transparent about data usage.
Best Practices: Clearly communicate the benefits of data sharing.
Use consent management software to ensure users know what data is being collected and how it will be used.
Utilizing Secure Data Management Tools
Implementation: Use secure CRM tools with built-in security features. These tools help manage data effectively while ensuring compliance with privacy regulations.
Best Practices: Choose CRM tools that provide encryption, access controls, and regular updates. Integrate CRM systems with other security tools for comprehensive data protection.
What is the future of data collection looks like?
AI and Data Collection Automation
AI-driven tools and automation technologies will significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of data collection processes.
These technologies will automate tasks, extract insights from unstructured data, and provide real-time analytics, making data collection faster and more reliable. The implementation of ISP proxies can further enhance data collection capabilities by providing a wide range of IP addresses.
Real-time data from IOT devices
IoT devices and adopting 5G networks will generate vast amounts of real-time data. This will enable continuous monitoring and proactive decision-making across various sectors, including healthcare, transportation, and environmental monitoring.
This will help businesses in all sectors create innovative products and services that solve people’s problems perfectly.
Higher Privacy and Ethical Standards
With the growing emphasis on data privacy, security, and compliance, regulations such as GDPR will continue to shape and keep data collection practices in control.
So it won’t get past the limit and erode people’s privacy.
Businesses need strong data control and governance and responsible AIpractices to ensure ethical data collection, solve privacy concerns, and maintain user trust.
Edge Computing
Edge computing will process data closer to its source, reducing slowness and improving the speed and accuracy of data collection.
This approach will be instrumental in remote or challenging environments, such as industrial settings or remote healthcare monitoring, enabling businesses to make faster and more informed decisions.
Centralized Data Markets
A shift will be towards creating centralized data hubs that provide on-demand, quality, verified, and fresh public data.
These data markets will achieve easier and more efficient data collection,
Helping businesses to solve customer needs, improve service quality, and predict market trends. The increased availability of verified public data will bring innovation and speed up industry decision-making.
Conclusion
Collecting data is going to be a lot easier.
At the same time, when businesses need data like never before, platforms like CDP (Customer Data Platform) and DMP (Data Management Platform) will get even more advanced.
They will help organizations get insights from tons of data in seconds and facilitate data integration with other tools.
This will make it easy to use the collected data to create personalized marketing campaigns that produce results.
Still, one cannot oversee this element - The security.
When data is collected, analyzed, stored, and shared at a large scale, privacy laws will become even stricter, forcing businesses to comply with them if they want to remain in business for the long term.
So yeah, Don’t screw up the security and privacy laws.
Question
If you’ve started collecting zero-party data, How are you using it to improve your marketing, product, or any aspect of the business?



