In the ever-evolving landscape of digital marketing and search engine optimization (SEO), staying ahead of the curve is paramount. While seasoned SEO professionals and digital marketers often rely on a familiar set of paid keyword research tools, there exists a treasure trove of FREE resources right at their fingertips—tools developed by the search giant that dominates the online realm.
These tools, offered by none other than Google, have the potential to reshape your approach to keyword research. The keyword research is basically nothing but understanding the user intent.
If you are a solopreneur or small and medium-sized business (SMB), you will find this article helpful. The tools covered here are either unfamiliar to you, or you might not be fully acquainted with how to leverage them to their maximum capabilities.
I guarantee that you can find semantic keywords, trending keywords, search volumes of keywords, user intent queries, and more without spending a single penny.
Google tools are a gold mine for keyword research if you know how to properly use it.
Why Google Tools for Keyword Research Matters?
Effective SEO revolves around optimizing content to align with user intent. Also, the content needs to be helpful and must provide real-value to the users. This is what Google’s Helpful content system states.
To cater user intent, it is essential to find the trend at the right time and understand user behavior.
How do you find trends at the right time and understand user behavior?
We all know that when seeking valuable insights into customer behavior and staying updated with current trends, there’s no better resource than the formidable data powerhouse—Google.
Google has a suite of dedicated tools for both keyword research and PPC campaigns under Think with Google website and Google Ads account.
In fact many of the paid Keyword tools rely on Google Ads API. The Google Ads account and its API is not only for ad campaigns research and management; but also for keyword research.
Hence, it is wise to understand the importance of Google suite of tools and make the most out of it. You can still go for paid tools, if you want a smoother user interface or more ease of use.
FREE Google Tools for Keyword Research
Google Trends for identifying trending consumer behavior
Google Keyword Planner for identifying LSI keywords and search volume of keywords
Alphabet Soup, aka Google auto suggest, to identify variations, synonyms, and related keywords
Google Bard AI for finding LSI keywords, potential new keywords, long-tail keywords, user intent and pain points
People Also Ask Section for finding the most searched questions about a topic.
Related Searches Section for finding additional user questions
Site Colon Method is for competitor analysis
Sitemap Exploration is for competitor analysis
Google Alerts is to stay informed about fresh content
Google Trends
Google Trends stands as a widely recognized tool for digital marketers and non-marketing professionals alike. What’s less commonly known is that Google Trends is part of the comprehensive toolkit offered by Think with Google.
Think with Google is an initiative by Google that provides insights, trends, and statistics pertaining to digital marketing, consumer behavior, and technology.
Okay, let’s delve into Google Trends.
Google Trends is a FREE effective tool that shows real-time trending search queries. It allows you to explore the relative search volume of specific keywords, topics, and queries across regions and languages.
In other words, Google Trends allows you to see what people are searching for during a particular timeline and in a particular region.
How to Effectively Use Google Trends for Keyword Research
1. Entering Topic or Search term: You can either input a specific search term or a topic. In case you are not sure about the specific keyword/ search term, you can go ahead with a broader perspective by giving the topic as input.
2. Comprehending the Data Visuals: Once you have given the input, you will be presented with a graph showing the trend over the time period that you have selected.
3. Compare Topic or Search term: Click “Compare” to compare your search terms or topics as shown in the screenshot below.
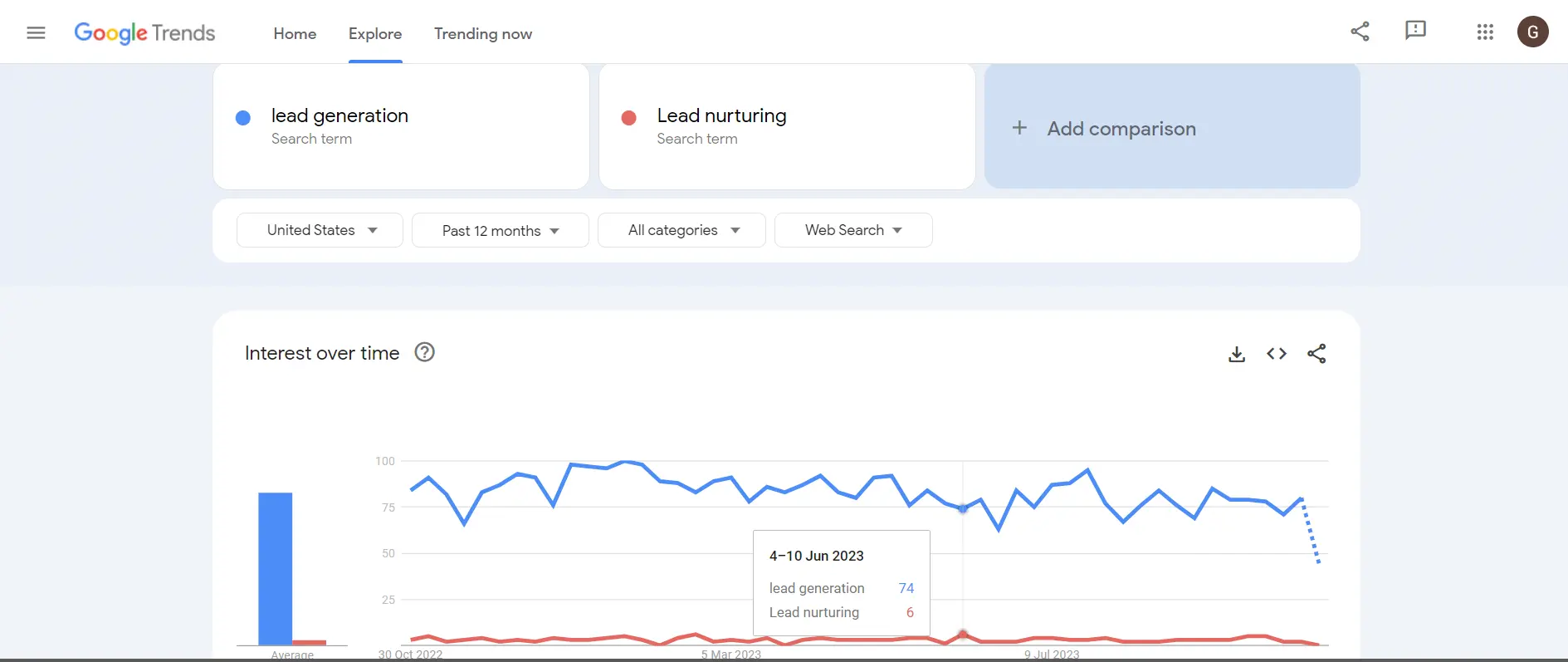
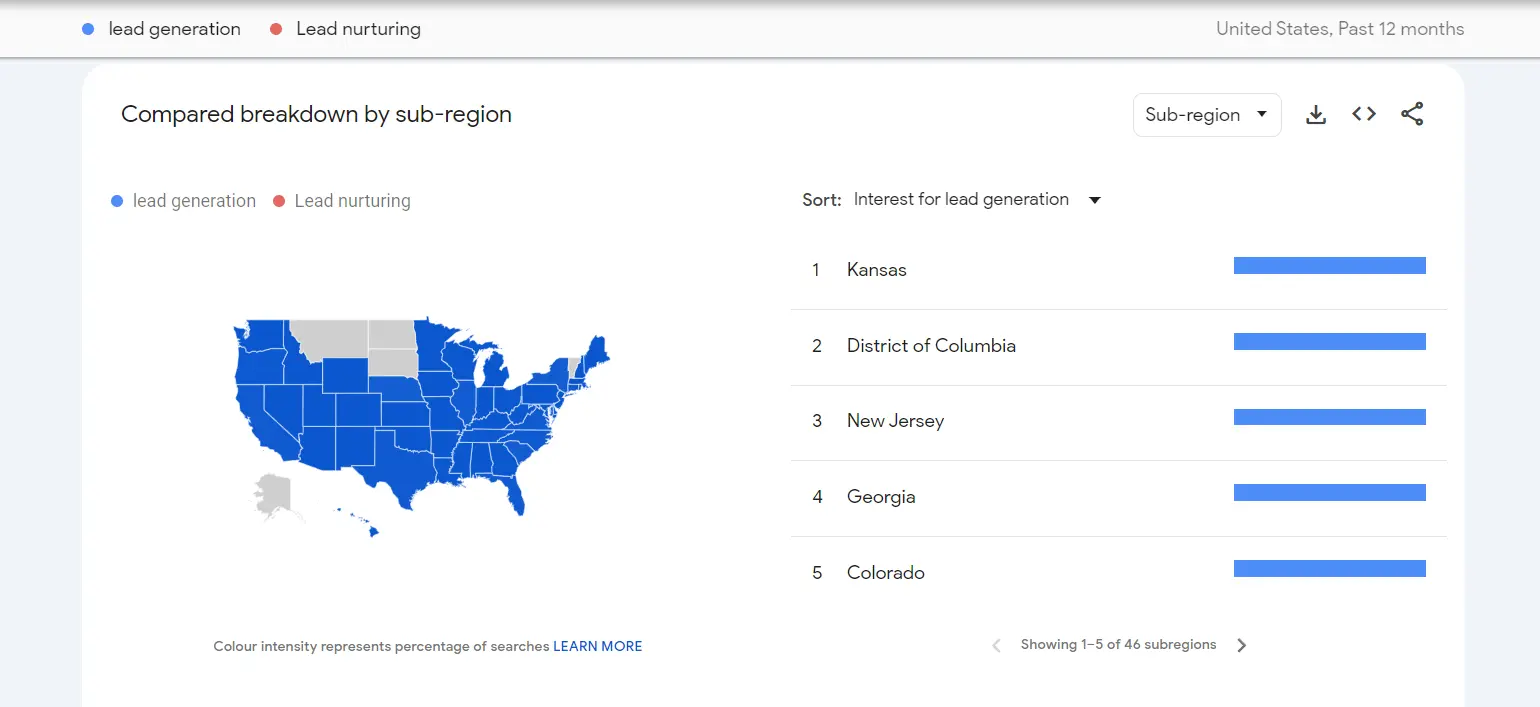
4. Segmentation Analysis: Scroll down a bit to reach “Compared breakdown by sub-region”. This section allows you to do segmented keyword research.
5. LSI Keywords: At the end of the page, you will see “Related topics” and “Related queries”. This is where you can find the Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords and long-tail keywords.
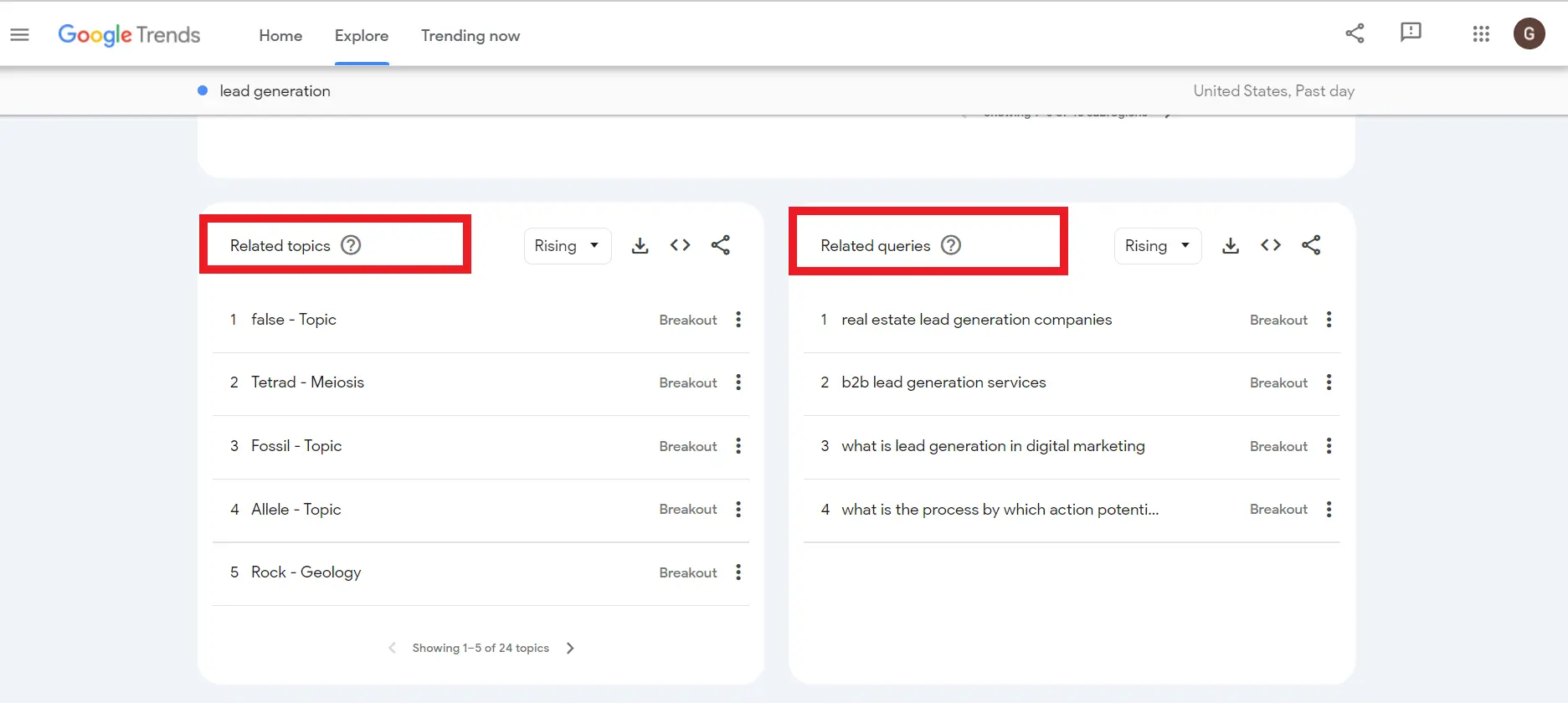
6. Understanding the Jargon: It is essential to know what 1-100 and breakout mean in Google Trends to further proceed with your keyword research.
On Google Trends, a score of 100 indicates the highest search interest for the selected term, considering both time and location.
Another less-known term is “breakout,” signifying a remarkable increase of over 5000% in searches for related topics or queries.
This is how you can find out what keywords are trending, LSI keywords, and long-tail keywords in Google Trends.
Google Keyword Planner
Google Keyword Planner is also a familiar tool amongst PPC experts and SEO specialists. It is one of the most popular tools in the suite offered by the Google Ads platform.
Unlike before, anyone with a Gmail account can access Google Keyword Planner. While primarily designed for Google Ads, the Keyword Planner is versatile and can also serve the purpose of keyword research. Unfortunately, many SEO experts often overlook its various features.
Neglecting to adjust the location filter is a common oversight, leading to suboptimal results in keyword research outcomes.
There are two separate section or tools inside Google Keyword Planner: one is used to find search volume of particular keywords and their forecasts, and the other one is used to find new semantic keywords—Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI)—as well as long tail keywords.
Apart from these, there are features, such as:
Among all these features, trend identification is one of my favorite features through which I have conquered SERPs many times.
To get to know all of these features within 6 minutes, check out our article: Keyword Planner for SEO Strategy: Revealing Overlooked Features. The article provides a step-by-step guide along with relevant screenshots.
Alphabet Soup, aka Google Auto Suggest
Alphabet Soup—aka Google Auto Suggest or Google Autocomplete—is one of the best ways to find great keywords for FREE.
Google Alphabet Soup is leveraging Google’s autocomplete feature to generate a list of potential keywords to a specific topic or search query.
The autocomplete suggestions represent a collection of related searches, essentially reflecting the queries conducted by other users.
The Google Alphabet Soup is one of the easiest ways to gather potential keywords and long-tail queries from users worldwide.
How to Use Google Alphabet Soup?
1. Type a specific keyword or a common search query
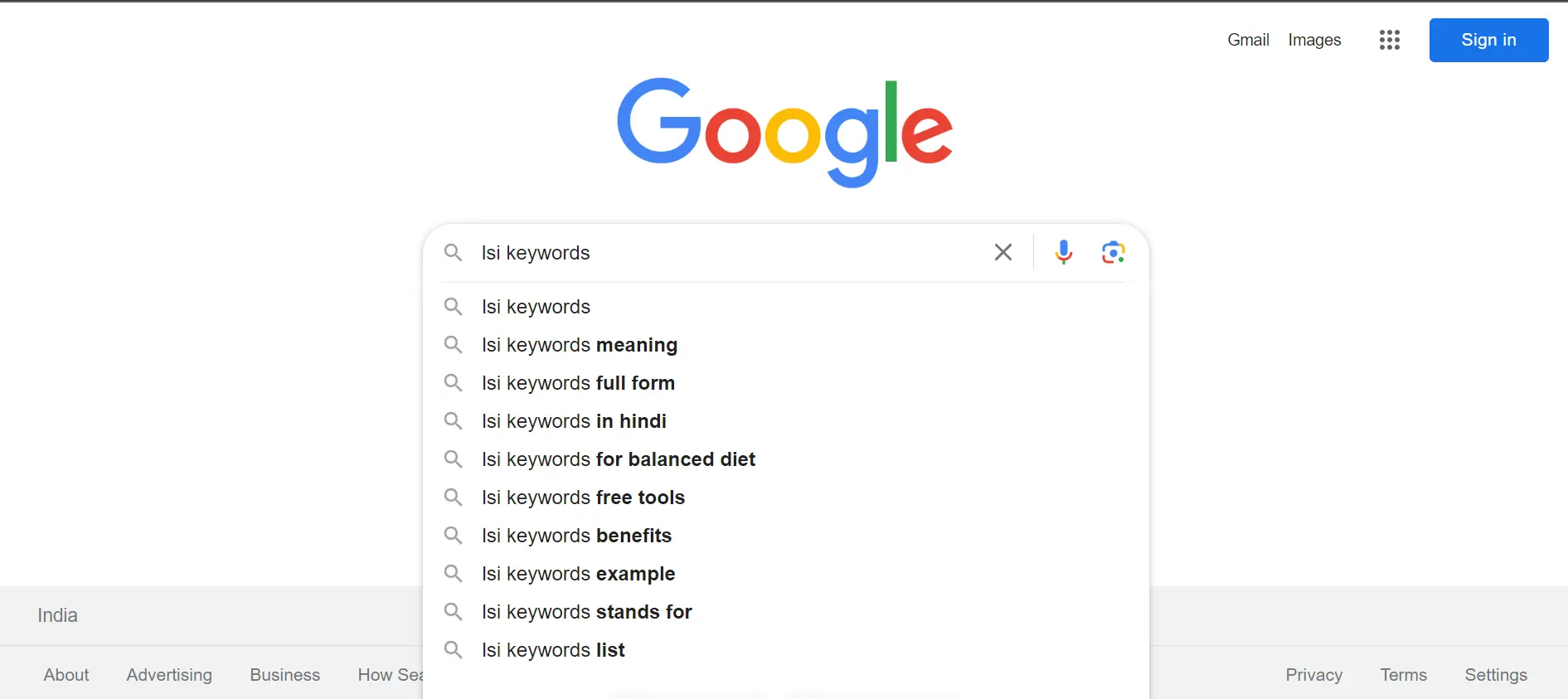
2. Observe the autocomplete suggestions
3. Templates to try for Top of the Funnel (TOFU) Content Ideas:

4. Templates to try for Middle of the Funnel (MOFU) Content Ideas:
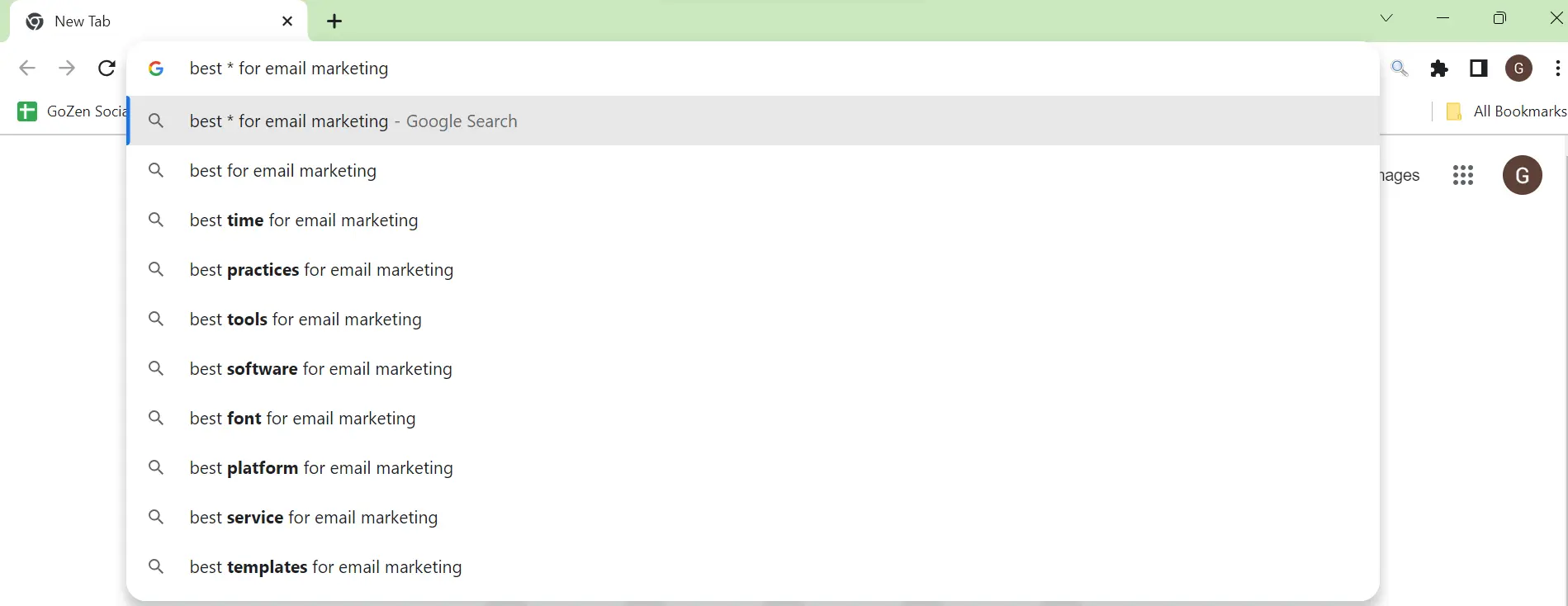
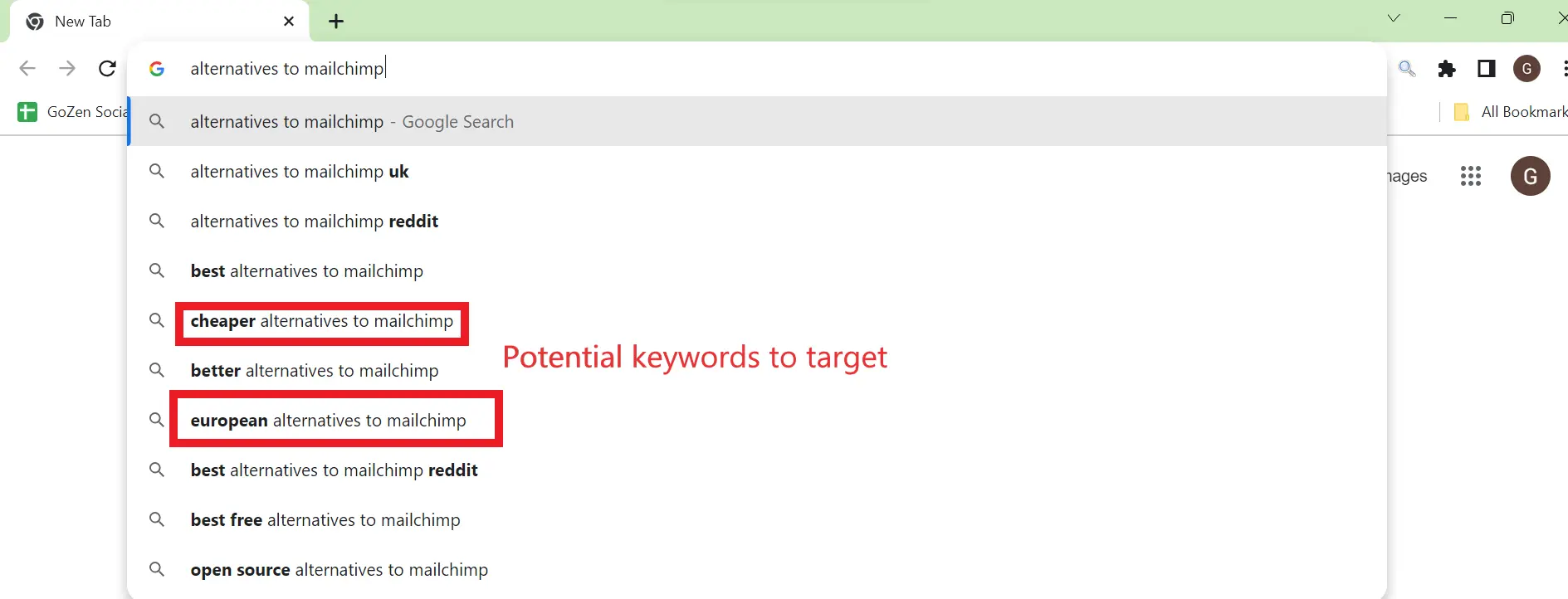
5. Templates to try for Bottom of the Funnel (BOFU) Content Ideas:
Creating content for the bottom of the funnel (BOFU) requires a different approach, and it’s essential to think from the customer’s point of view.
Hence, there is only a limited template you can use for this purpose.
a. Alternatives to + “Brand or Seed keyword”
Google Bard AI
In the midst of the AI era, it’s impossible not to catch the wave of innovation that is Google Bard AI.
Google Bard is an interactive chat-based generative AI tool that is powered by the large language model (LLM), PaLM 2.
Generative AI models are sophisticated AI models that generate text, images, video, audio from text descriptions known as prompts.
You can leverage Google Bard to gather:
How to Use Google Bard AI for Keyword Research
1. Head to Bard website and sign in with your Gmail account.
2. Enter the prompt to perform certain tasks: You can use the below prompts to interact with the Google Bard for effective keyword research.
3. Prompt to discover new keywords: Generate a list of relevant keywords for a [your niche or topic] website
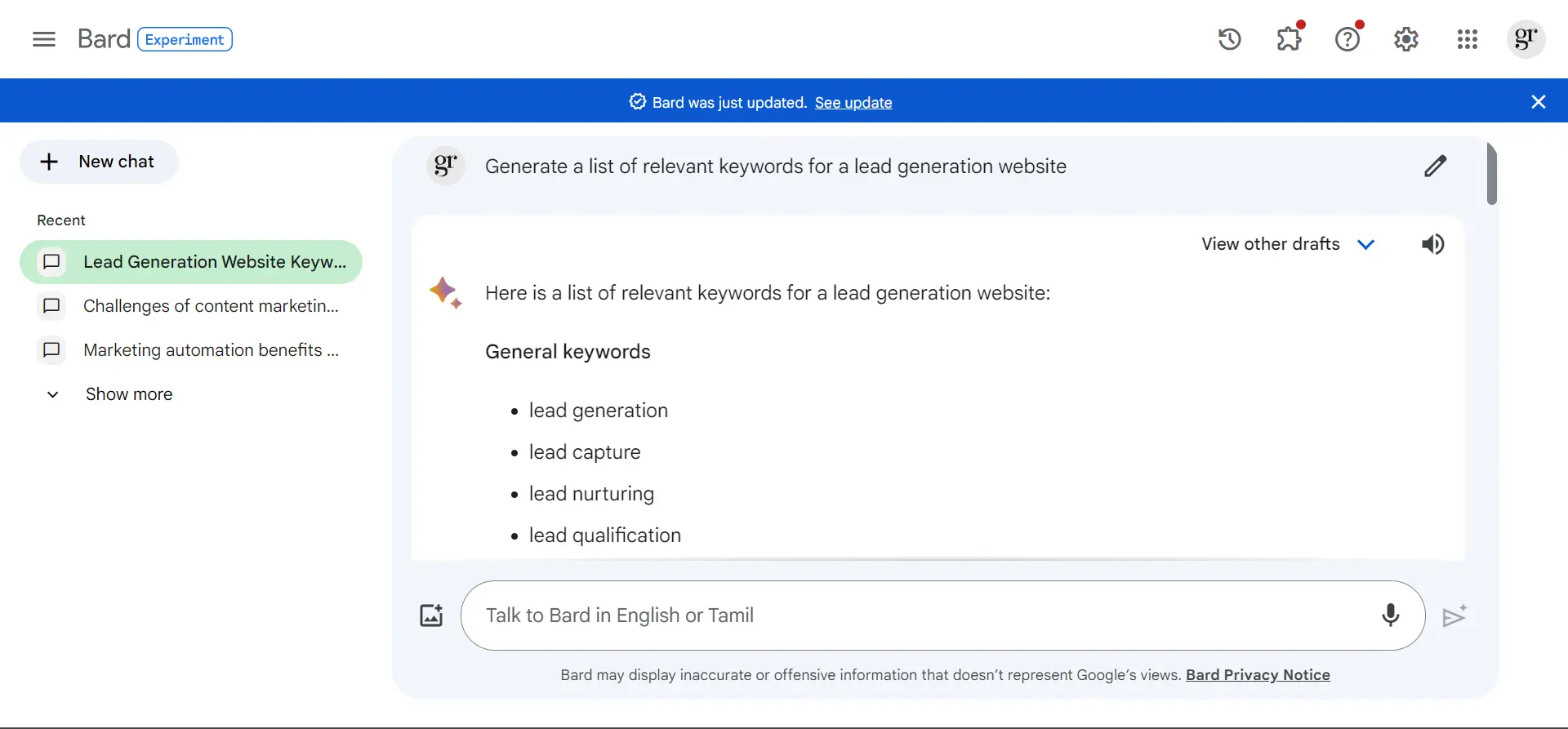
For more information on the Bard’s response to my query: https://g.co/bard/share/5ed90f2adccc
4. Prompt to discover semantic keywords: Generate variations of the keyword [your main keyword] to include different phrasings, synonyms, and semantic keywords.
5. Prompt to discover long-tail keywords: Discover long-tail keywords for [specific aspect or feature] in [your industry]
6. Prompt for competitor analysis: Provide insights into keywords targeted by [competitor’s name] in [industry/niche].
7. Prompt to understand user intent: Analyze user intent for searches related to [your main topic] and suggest keywords that align with that intent
8. Prompt to understand customer pain points: Identify common pain points experienced by customers in [your industry/niche]. Generate insights into the challenges and frustrations users face when [engaging with/buying/using] [your product/service].
Once you gather a list of keywords from Bard, ensure to insert it into Google Keyword Planner to gain insights, such as search volumes and more new semantic keywords.
People Also Ask (PAA) Section
People Also Ask (PAA), aka related questions group, is a collection of similar questions related to the search query of what the user typed in lately.
PAA is dynamically generated using the knowledge graph algorithm that identifies common questions related to the user’s search query, providing a more interactive and dynamic search experience.
This section usually appears just below the first result in Google SERP. Typically, the section comprises four questions. Upon examining the final question, Google will automatically present a new set of questions.
Exploring the People Also Ask section is the best way to find most searched questions about a topic.
How to Use People Also Ask Section Effectively?
All you have to do is type in your seed keyword or semantic keywords in the Google search box and gather as many People Also Ask questions as possible.
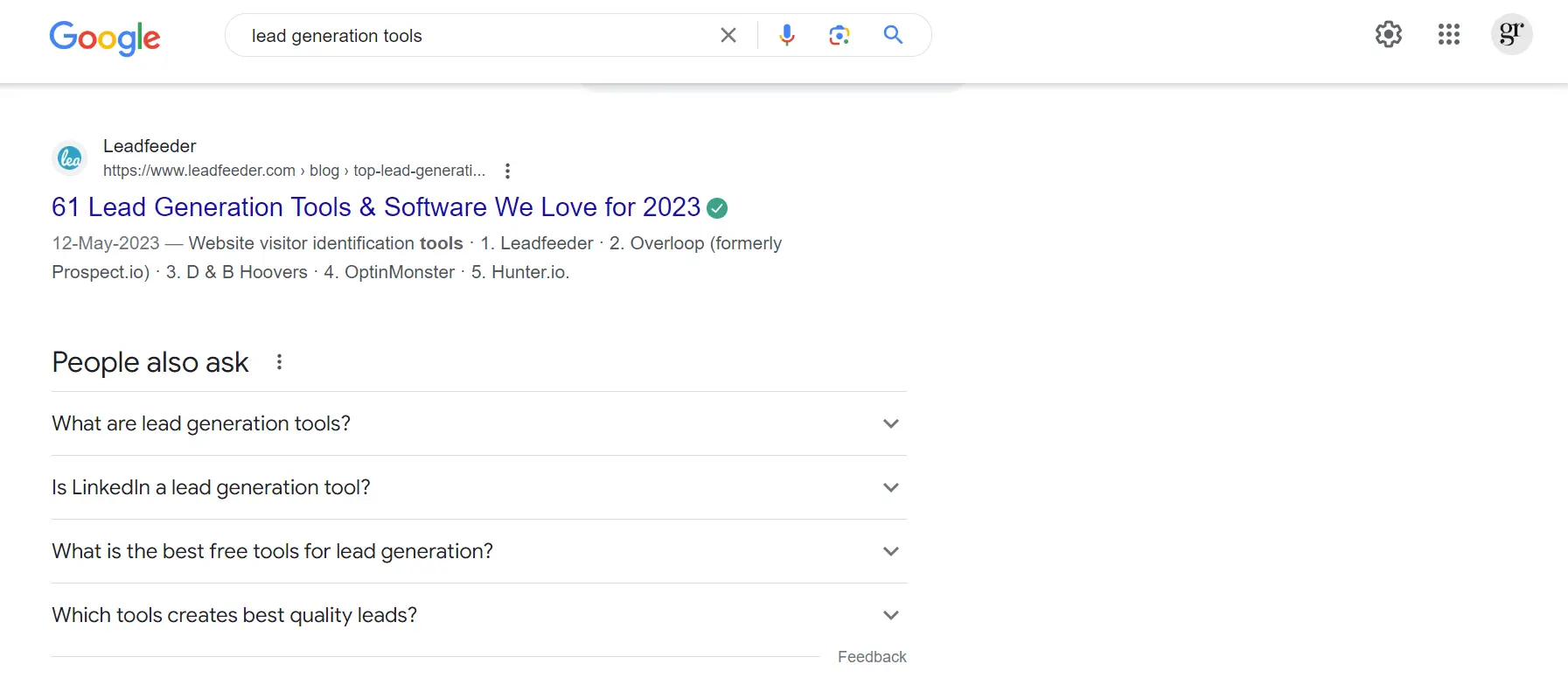
After compiling all the questions, you can respond to them indirectly within a specific section of your article, or alternatively, address them directly by incorporating the exact questions into a dedicated Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) section.
Related Searches Section
The Related Searches Section of Google SERP is a list of additional queries that are related to the user’s original search term.
Clicking on one of the related searches will initiate a new search query, providing the user with a set of results tailored to the selected related search term.
It usually appears at the bottom of the SERP page. Since Google recently launched the Continuous scrolling feature, you can find this section after ten results.
Exploring Related Searches Section is a good way to expand your keyword list since it gives synonyms and variations of your seed keyword. You can also use it to analyze what terms your competitors are targeting.
How to Use Related Searches Section?
1. Enter your seed keyword or any semantic keywords
2. Scrolling down to reach the Related Searches Section
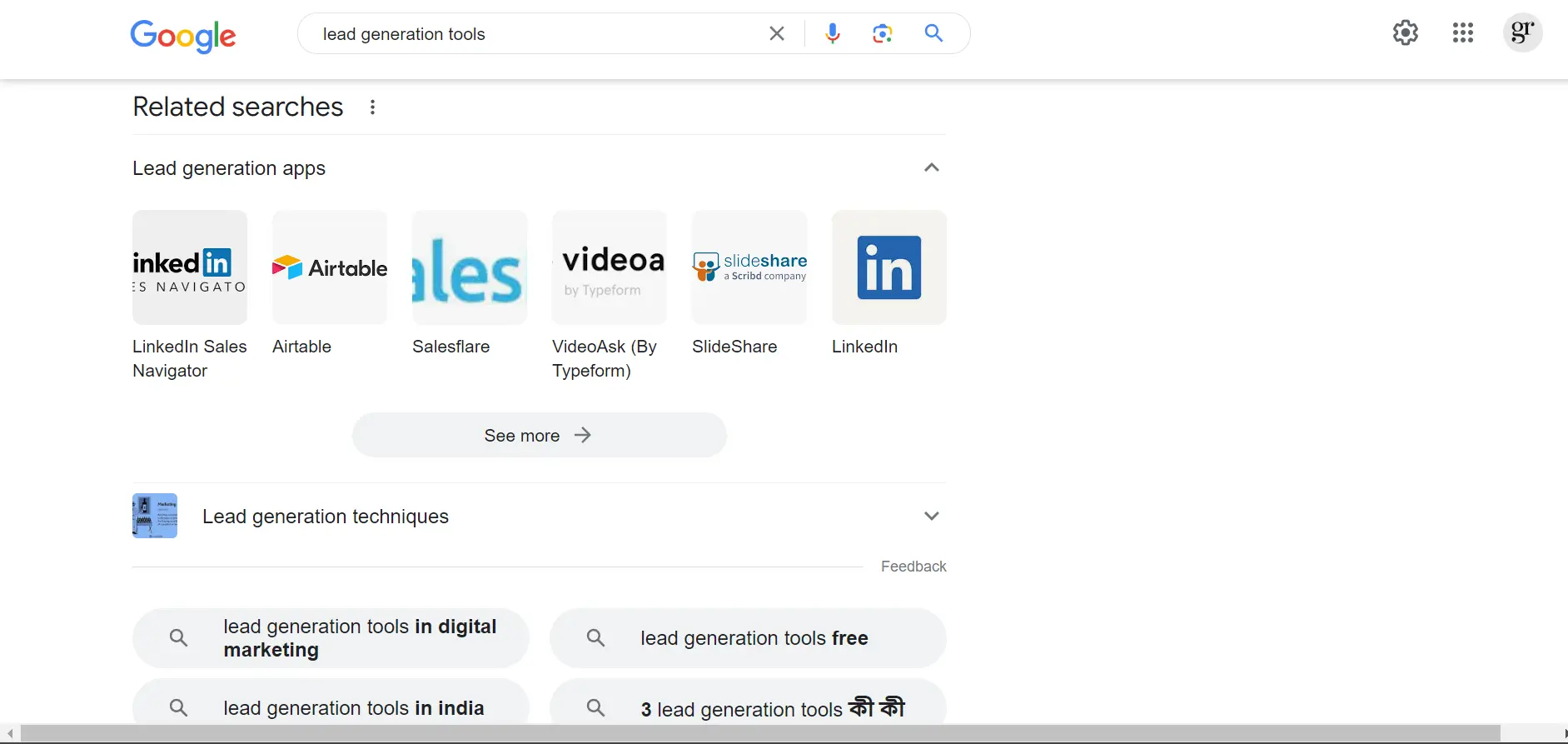
That’s it. Simple.
Site Colon Method
Site Colon is an advanced search operator that is used to find indexed pages of a specific website. It can be used to gain insights of your competitor website’s indexed content and the keywords associated with it.
This Site Colon is not a standalone keyword research tool. However, it can be a supplementary approach to gather insights into a website’s content and the keywords associated with it.
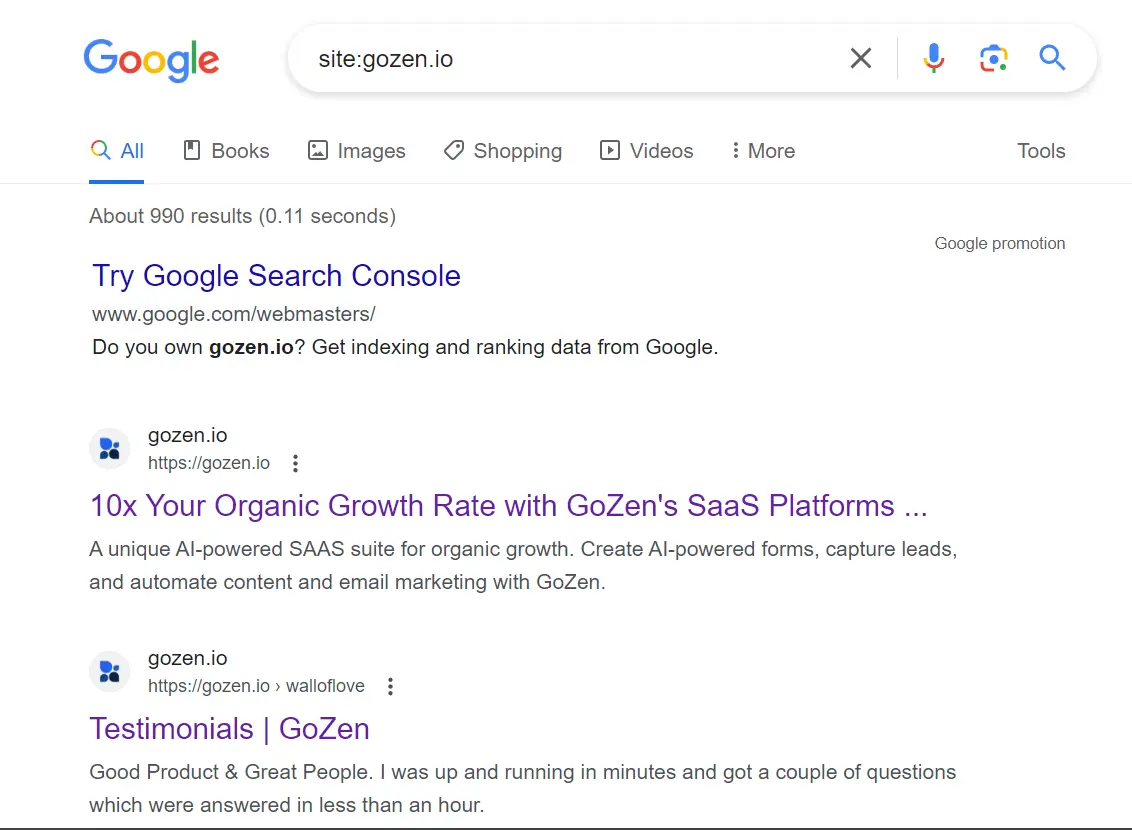
How to Use Site Colon Method for Keyword Research?
1. Syntax: site:competitor.com. It displays all the indexed pages of the site “competitor”.com. You can type in the syntax manually or use an extension called “Search the current site”.
2. You can even fine-tune the results by adjusting the syntax as shown below:
1. Site:competitor.com/blog
3. Now, go through all the meta descriptions and titles to identify the competitor keywords.
Sitemap Exploration
Sitemap exploration is one of the most underestimated techniques, which can be used as an alternative to the Site Colon method discussed above.
Sitemap is a file that lists all the pages of a website and provides information about its organization and structure.
Every company or website on the web must have a proper sitemap as an ethical practice of SEO.
By exploring a sitemap of your competitor, you can identify:
How to Use Sitemap Exploration for Keyword Research
1. Use the following syntax https://competitor.com/sitemap.xml to explore the sitemap of your competitors. In case you are caught up with page not found error, try adding sitemap-0.xml or sitemap-1.xml, or sitemap-index.xml
2. To find topical authority and content volume, explore the content hierarchy and categories section of the sitemap
3. Search “last modified” to identify the latest change they made, which can be a trending topic to cover on
4. Explore different section of the sitemap to find new keywords
Google Alerts
Introduced by Google on August 6, 2003, Google Alerts is a longstanding service that detects changes in content and notifies users accordingly.
Unlike Google Trends, which analyzes real-time trends, Google Alerts focuses on providing notifications about new content related to specified keywords in Google’s search results. This notification service keeps users informed whenever there is fresh content matching their defined criteria.
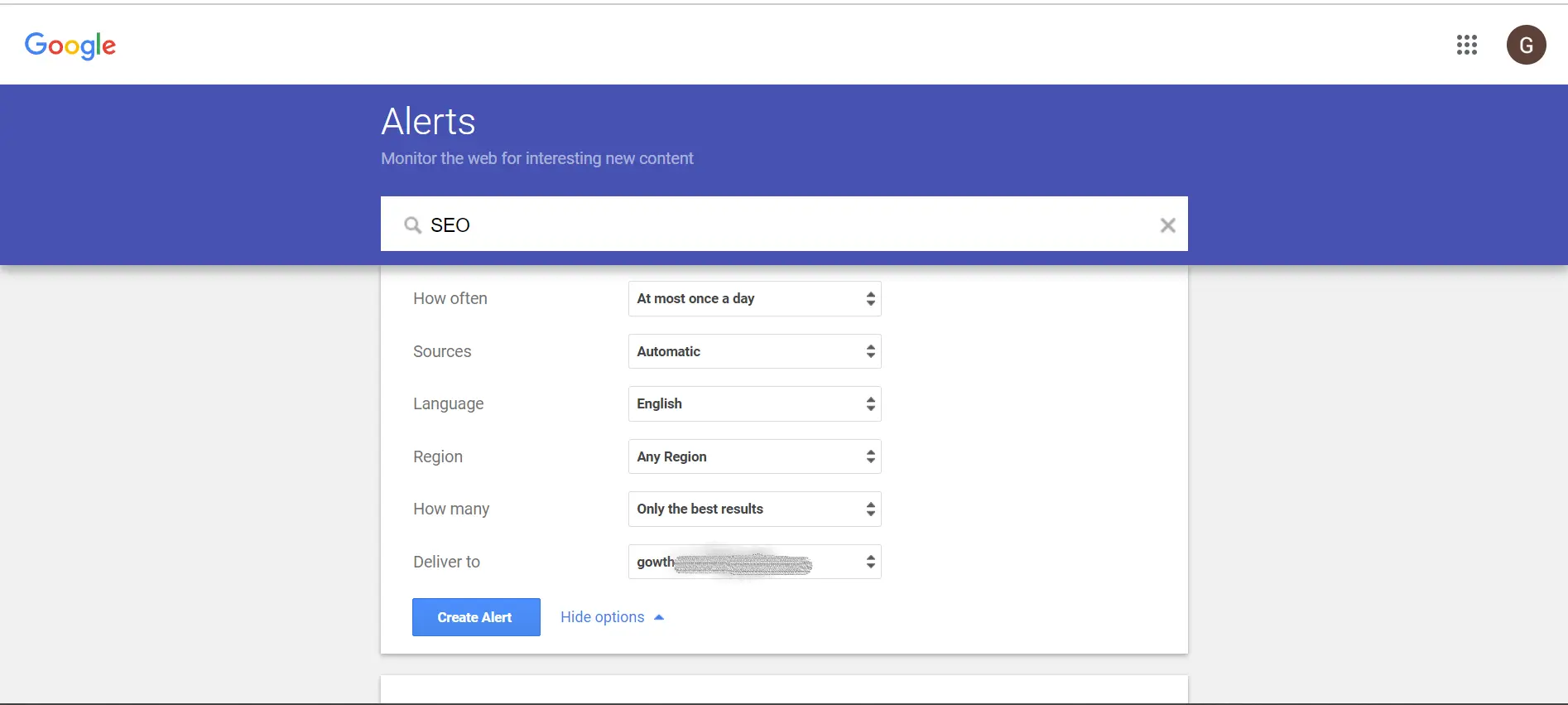
How to Use Google Alerts for Keyword Research?
FAQs
1. How do I find SEO keywords for FREE?
Anyone can find potential SEO keywords for their niches, without even spending a single penny.
Yes, there are numerous Google tools and features available for everyone to utilize in conducting comprehensive keyword research:
2. Is there a fee to use Google’s keyword research tool?
Anyone can use Google’s keyword research tool free of cost. All you need is a Gmail account to access the suite of Google tools.
You can even access a few Google tools/ features without a Gmail account.
3. What is the difference between People Also Ask (PAA) and Related Searches Section?
While both the PAA and Related Searches sections aim to assist users in finding relevant information, they do so in slightly different ways.
PAA offers a dynamic set of questions related to the user’s query, while the Related Searches section provides additional search term suggestions for users looking to explore related topics.



